Comprehending the intricacies of the chest muscles is critical for anyone looking to enhance their upper body strength and overall physique. The pectoral region is comprised of several critical muscles that play a pivotal role in everyday movements and athletic performance. Understanding the functions of the pectoralis major and pectoralis minor muscles can help individuals optimize their workouts and prevent injuries. In this detailed guide, we will delve into the anatomy of the chest, highlighting the key muscles and their functions to provide you with a comprehensive understanding of this vital muscle group.
Major Muscles of the Chest
Pectoralis Major
For the chest to perform powerful movements like pushing and hugging, the Pectoralis Major muscle comes into play. This large, fan-shaped muscle is situated in the upper chest area and is responsible for the majority of the chest’s mass and shape. The primary function of the Pectoralis Major is to bring the arms across the body, as in pushing movements such as bench presses or chest flies.
Chest exercises that target the Pectoralis Major are crucial for building upper body strength and a well-defined chest. Incorporating movements like bench presses and push-ups into your workout routine can help develop and strengthen this essential muscle.
Pectoralis Minor
Pectoralis Minor is a smaller, triangular muscle located underneath the Pectoralis Major. Despite its size, this muscle plays a vital role in shoulder movement and stability. The Pectoralis Minor assists in pulling the shoulder forward and downward, aiding in movements like reaching forward or downward.
Chest workouts that engage the Pectoralis Minor can help prevent shoulder injuries and improve overall shoulder function. Strengthening this muscle through exercises like push-ups and dips can contribute to better posture and upper body mobility.
Movements
Serratus Anterior
Pectoralis and the Serratus Anterior work together to protract the scapula, allowing movements like pushing away from the body. The Serratus Anterior muscle is crucial for shoulder blade stability and plays a significant role in overhead movements. Strengthening this muscle can enhance shoulder function and prevent shoulder injuries.
Pectoralis and the serratus anterior are often worked synergistically in exercises such as push-ups and overhead presses. Focusing on maintaining proper form and engaging these muscles during workouts can lead to improved upper body strength and stability.
Subclavius
For shoulder stability and protection, the Subclavius muscle acts as a support system. This small muscle runs along the clavicle, helping to stabilize and protect the shoulder joint during movements. Strengthening the Subclavius can contribute to improved shoulder health and reduce the risk of shoulder injuries.
For individuals involved in activities that place high demands on the shoulders, such as weightlifting or overhead sports, targeting the Subclavius through specific exercises like shoulder shrugs and overhead carries can be beneficial for overall shoulder stability and function.
Supporting Muscles and Structures
Your chest is supported by a complex web of muscles and structures that play a crucial role in various movements and functions. Understanding these supporting elements is essential for overall chest strength and stability.
Intercostal Muscles
On either side of the ribcage, lie the intercostal muscles. These muscles play a vital role in the mechanics of breathing, as they help expand and contract the ribcage during inhalation and exhalation. There are three layers of intercostal muscles: external, internal, and innermost, each contributing to the movement of the ribcage.
These muscles are essential for proper respiratory function and provide support to the ribcage during physical activities that require deep breathing or trunk rotation. Keeping these muscles strong and flexible is key to maintaining optimal chest mobility and overall lung capacity.
Clavicle and Ribcage
Structures supporting the chest also include the clavicle and ribcage. The clavicle, or collarbone, serves as a crucial bony structure that connects the arm to the body and provides support for shoulder movement. The ribcage, consisting of 12 pairs of ribs, protects the vital organs within the chest cavity and aids in breathing.
The clavicle and ribcage create a protective framework for the chest, helping to maintain its shape and structure. Any injuries to these structures can have serious implications for chest stability and overall functionality. Proper posture and strengthening exercises can help maintain the health and integrity of these essential structures.
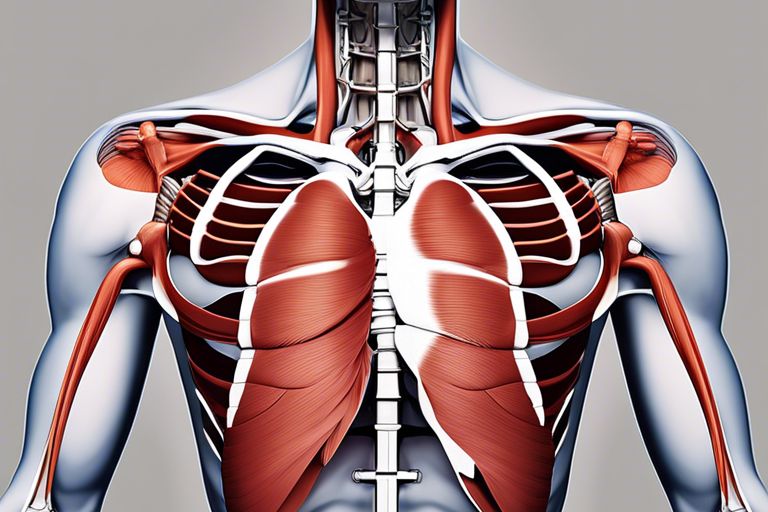
Common Injuries and Prevention
Despite the chest being a strong and resilient area of the body, it is still susceptible to injuries, especially during strenuous physical activities or due to overuse. Understanding common injuries and how to prevent them is crucial in maintaining chest health and overall well-being.
Strains and Sprains
The chest muscles can experience strains and sprains, which are common injuries that occur due to sudden stretching or tearing of the muscle fibers. Strains typically result from overexertion or improper lifting techniques, leading to muscle pain and weakness. Sprains, on the other hand, involve the stretching or tearing of ligaments that connect bones and stabilize joints, causing discomfort and limited range of motion.
The key to preventing strains and sprains in the chest is to maintain proper form during exercises and activities that engage the chest muscles. Gradually increase the intensity and duration of your workouts to prevent overloading the muscles. Additionally, incorporating adequate rest periods and stretching exercises can help improve flexibility and reduce the risk of injury.
Rehabilitation and Exercises
Common rehabilitation techniques for chest injuries include rest, ice therapy, compression, and elevation to reduce pain and inflammation. Controlled movements and gentle stretches can help restore flexibility and strength in the affected muscles. Exercises such as chest presses, push-ups, and dumbbell flyes can aid in rebuilding muscle endurance and function.
Any rehabilitation program for chest injuries should be supervised by a healthcare professional or certified trainer to ensure proper healing and prevent further damage. It is essential to follow a customized exercise plan that gradually progresses in intensity to avoid re-injury and promote a full recovery of the chest muscles.
Conclusion
Considering all points discussed, the chest muscles play a crucial role in various upper body movements and functions. Understanding the anatomy of the chest muscles, such as the pectoralis major and minor, serratus anterior, and the intercostal muscles, is essential for anyone looking to improve their chest strength and overall upper body performance. By incorporating targeted exercises and proper form, individuals can effectively strengthen and develop their chest muscles to support activities such as pushing, lifting, and maintaining good posture. Overall, an awareness of the key chest muscles and their functions is key to achieving a well-rounded and balanced upper body strength training regimen.
FAQ
Q: What are the key muscles of the chest?
A: The primary muscles of the chest include the pectoralis major and pectoralis minor. The pectoralis major is the large, fan-shaped muscle that makes up most of the chest wall, while the pectoralis minor is a smaller muscle that lies underneath the pectoralis major. Both of these muscles play a crucial role in movements like pushing and lifting.
Q: What functions do the chest muscles perform?
A: The chest muscles are responsible for a variety of crucial functions. The pectoralis major is involved in movements such as pushing, bench pressing, and hugging. It also helps with shoulder movement and stability. The pectoralis minor, on the other hand, assists in stabilizing the scapula and helps with movements like raising the ribs during breathing.
Q: How can I strengthen my chest muscles?
A: There are several exercises you can do to strengthen your chest muscles, including bench presses, push-ups, chest flies, and dips. It’s important to vary your workouts and target different areas of the chest to ensure overall muscle development. It’s also crucial to maintain proper form and gradually increase weight and intensity to avoid injury and see optimal results.